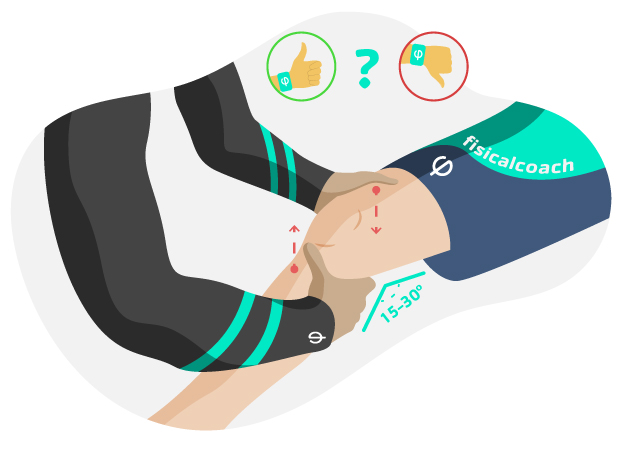
Lachman test
This test is used to assess the degree of damage to the stability of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
- Required material: A physiotherapy table. If the test is performed on the floor, a mat or matting is required.
- Procedure: The subject must lie in the supine position (face up) and the assessor faces the knee to be assessed. The assessor should place the knee in 15° of flexion from knee extension. One hand should be placed at the level of the anterior part of the lower third of the thigh to stabilise it, while the other hand should hold the upper third of the thigh. From this position, apply a force with the aim of provoking an anterior tibial dislocation.
- Assessment: The test shall be considered abnormal or positive when there is excessive displacement of the tibia relative to the femur. Otherwise, the test shall be considered normal or negative.
- Remarks: Other knee structures such as the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), meniscus, etc. should also be assessed for involvement or damage.
Take this test and 139 more in our App